handle custom script azure extension
The secret of getting ahead is getting started. - Mark Twain
handle custom script azure extension
Battling Terraform’s Azure VM Extension Nightmares: A Developer’s Survival Guide
By Tech Columnist
Picture this: It’s Tuesday morning. Coffee in hand, you sit down ready to deploy your latest infrastructure changes. You run your Terraform apply command with confidence, only to be greeted by a wall of red text. Sound familiar? Today, I’m diving into one of the most frustrating yet common issues when managing Azure infrastructure with Terraform: the dreaded VM extension conflicts.
The Phantom Extension Problem
Recently, I encountered a scenario that many cloud engineers will recognize. My Terraform deployment was failing with this error:
Error: A resource with the ID "/subscriptions/[redacted]/resourceGroups/app_rg_uat/providers/Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/web-uat-0/extensions/BuildAndUpgradeScripts" already exists - to be managed via Terraform this resource needs to be imported into the State.
This is classic Terraform behavior when it tries to create a resource that already exists in your cloud environment but isn’t tracked in your Terraform state. In this case, a CustomScript extension was somehow created outside of Terraform’s knowledge.
The Extension Execution Failure
The plot thickened when attempting to deploy to another VM in the same environment:
Error: creating/updating Extension: polling after CreateOrUpdate: polling failed: the Azure API returned the following error: Status: "VMExtensionProvisioningError" Code: "" Message: "VM has reported a failure when processing extension 'BuildAndUpgradeScripts'...
The extension was trying to execute a script that was failing with a non-zero exit code. Classic.
The Solution: Clean Slate Approach
After troubleshooting numerous potential causes (permission issues, script errors, network problems), the solution turned out to be surprisingly straightforward but required a two-pronged approach:
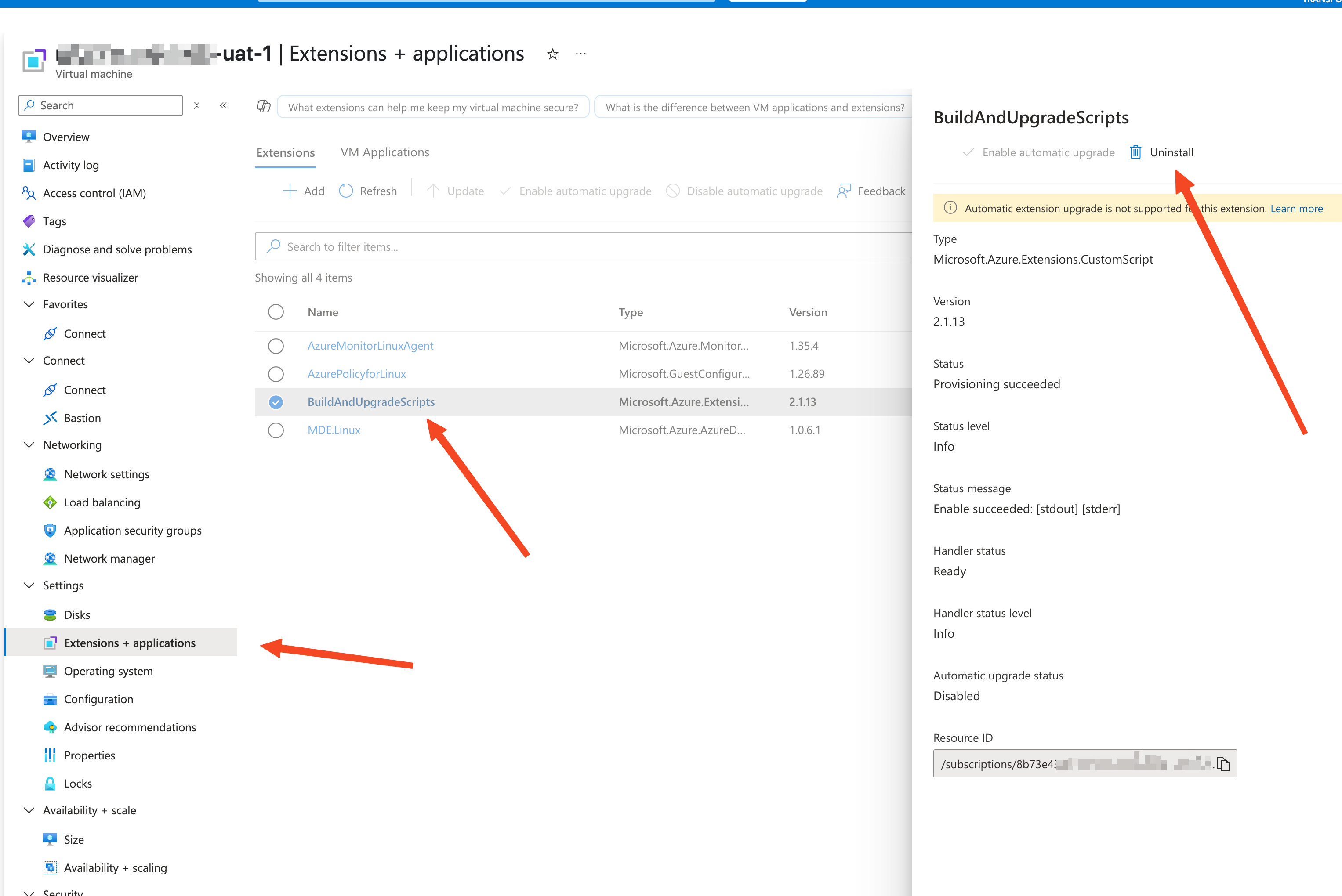
- Uninstall the rogue extensions via the Azure Portal:
- Navigate to the Virtual Machine in the Azure Portal
- Find the extensions section
- Locate the problematic CustomScript extension
- Click “Uninstall” to remove it from the VM
- Clean up script artifacts on the VM:
- SSH into the affected Linux VM
- Remove any script files that might have been downloaded by previous extension runs:
sudo rm /usr/local/bin/build_server.sh - Re-run your Terraform pipeline
Why This Works
This approach addresses both sides of the problem:
- Uninstalling the extension from Azure removes the resource that was causing the “already exists” error
- Cleaning up the script files ensures there are no leftover artifacts causing execution conflicts
Lessons for Cloud Engineers
This experience highlights several important principles when working with IaC tools like Terraform:
-
State Management is Everything: Always check for drift between your Terraform state and the actual cloud environment. Consider using
terraform importto bring rogue resources under management. -
Extensions Are Stateful: VM extensions in Azure maintain state both in Azure’s control plane and on the VM itself. Remember to clean both sides.
-
Check the Logs: When troubleshooting CustomScript extensions, the error messages can be cryptic. SSH into the VM and check
/var/log/azure/for more detailed logs. -
Portal as Last Resort: While we rely on IaC, sometimes the quickest path to resolution involves manual intervention through the portal. Don’t be afraid to use it as a troubleshooting tool.
The next time you face the “resource already exists” error or an extension provisioning failure, try this clean slate approach. It might save you hours of debugging and keep your deployment pipeline flowing smoothly.
What’s your most challenging Terraform scenario? Share in the comments below!
This article is based on real-world experiences with cloud infrastructure management. Company and subscription details have been redacted for privacy.

